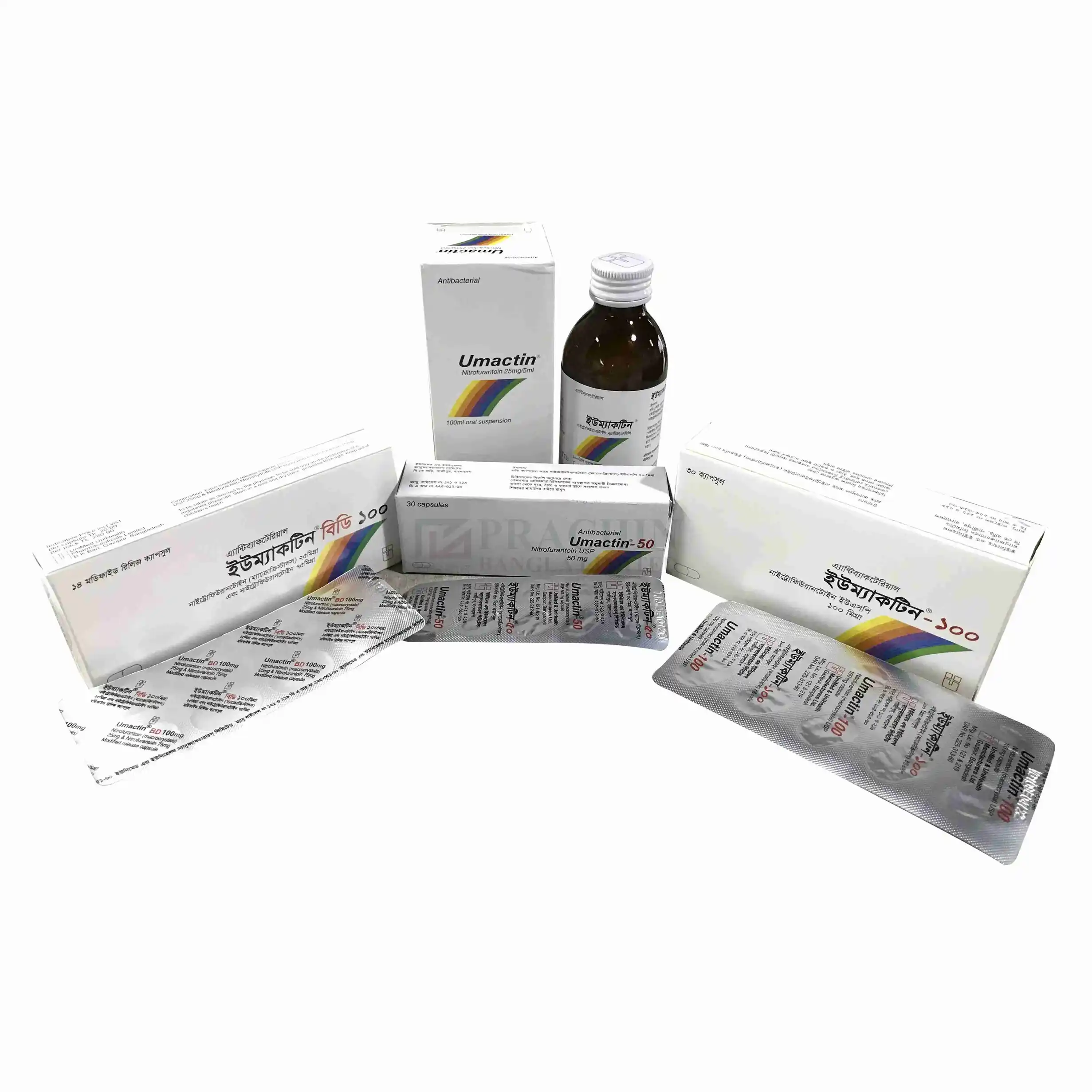
Introduction
Umactin is an antibiotic that
fights bacteria. It is used to treat and prevent uncomplicated urinary tract
infections. It works by killing the bacteria that cause such disease. But, it
will not treat a viral infection. Umactin should be taken in the dose and duration
as advised by the doctor. You may take it with food to avoid nausea, which is a
common side effect. It is better to have this medicine at the same time each
day to get the most benefit and you should keep on taking this medicine for as
long as you are prescribed it, even if your symptoms quickly improve. If you
stop taking it too early the infection may return or worsen. Some people may
develop side effects like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects
are usually temporary and go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the
medicine. Consult your doctor if these side effects bother you or do not go
away. This medicine may turn your urine into dark yellow or brown color. But,
this is normal and nothing to worry about. Before starting treatment with this
medicine, you should tell your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding or
suffering from any liver, kidney or heart problems or if you are allergic to
any antibiotic.
Uses of Umactin
Bacterial infections of urinary
tract
Side effects of Umactin
Common
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
How to use Umactin
Take this medicine in the dose
and duration as advised by your doctor. Swallow it as a whole. Do not chew,
crush or break it. Umactin is to be taken with food.
How Umactin works
Umactin is an antibiotic. It
works by killing the bacteria in the urine that causes infection.
What if you forget to take
Umactin?
If you miss a dose of Umactin,
take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose,
skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the
dose.
Quick Tips
Niftas Tablet SR treats and
prevents uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Finish the prescribed course of
the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Stopping it early may make the
infection come back and harder to treat.
Take it with food to avoid
nausea, which is a common side effect.
It can turn your urine a dark
yellow or brown colour. This is normal and nothing to worry about.
Do not take it for longer or more
often than prescribed by your doctor.
Brief Description
Indication
Uncomplicated UTI, Urinary Tract
Infection
Administration
Should be taken with food. Take
w/ or immediately after meals. Sustained release macrocrystals indicated only
for patients >12 years for acute UTIs (cystitis) caused by E coli or S
saprophyticus
Adult Dose
Oral Acute uncomplicated urinary
tract infections Adult: 50-100 mg 4 times daily for 7 days or for 3 days after
obtaining sterile urine. SR preparation: 100 mg bid for 7 days or for 3 days
after obtaining sterile urine. Prophylaxis of uncomplicated urinary tract
infections Adult: 50-100 mg at bedtime for up to 12 months.
Child Dose
Urinary Tract Infection >1
month 5-7 mg/kg/day PO divided q6hr for 7 days UTI prophylaxis: 1-2 mg/kg PO
qHS or 2 divided doses >12 years 50-100 mg PO q6hr for 7 days or for 3 days
after obtaining sterile urine SR preparation: 100 mg PO q12hr for 7 days or for
3 days after obtaining sterile urine Long-term prophylaxis/suppression: 50-100
mg PO at bedtime for up to 12 months
Renal Dose
Loses effectiveness in patients
with CrCl <60 mL/min due to inadequate urine concentration Monitor renal
function; renally excreted; decreased renal function more likely in elderly
Contraindication
Severe renal impairment (anuria,
oliguria, significantly elevated serum creatinine, CrCl <60 ml/min).
Hypersensitivity to nitrofurans, G6PD deficiency, infants <3 mth. Pregnancy
at term, during labour and delivery, or when the onset of labour is imminent.
Mode of Action
Nitrofurantoin interferes with
cell metabolism and cell wall synthesis by inhibiting several enzyme systems
including acetyl coenzyme A. It is bactericidal to most gram-positive and
gram-negative urinary tract pathogens.
Precaution
Elderly. Monitor hepatic and
pulmonary function during prolonged therapy. Pre-existing pulmonary, hepatic,
neurological, or allergic disorders, predisposition to peripheral neuropathy
e.g. renal impairment, anaemia, DM, electrolyte imbalance, debility, vitamin B
deficiency. Withdraw if signs of peripheral neuropathy occur. Lactation.
Lactation: Enters breast milk; discontinue drug or do not nurse
Side Effect
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia,
abdominal pain, diarrhoea; headache, drowsiness, vertigo, dizziness, nystagmus,
benign intracranial hypertension; rash, urticaria, pruritus, fever,
sialadenitis, angioedema, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis,
pancreatitis, lupus-like syndrome, myalgia, arthralgia; acute pulmonary
sensitivity reactions; megaloblastic anaemia, leucopenia, granulocytopenia or
agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anaemia, haemolytic anaemia (in
G6PD-deficient patients); transient alopecia; brownish discolouration of urine.
Potentially Fatal: Peripheral polyneuropathy, hepatotoxicity, anaphylaxis,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis.
Interaction
Reduced excretion with probenecid
or sulfinpyrazone. Absorption reduced by magnesium trisilicate. Antagonistic
effects with quinolone antibacterials. Reduced effects with carbonic anhydrase
inhibitors or urinary alkalinisers.