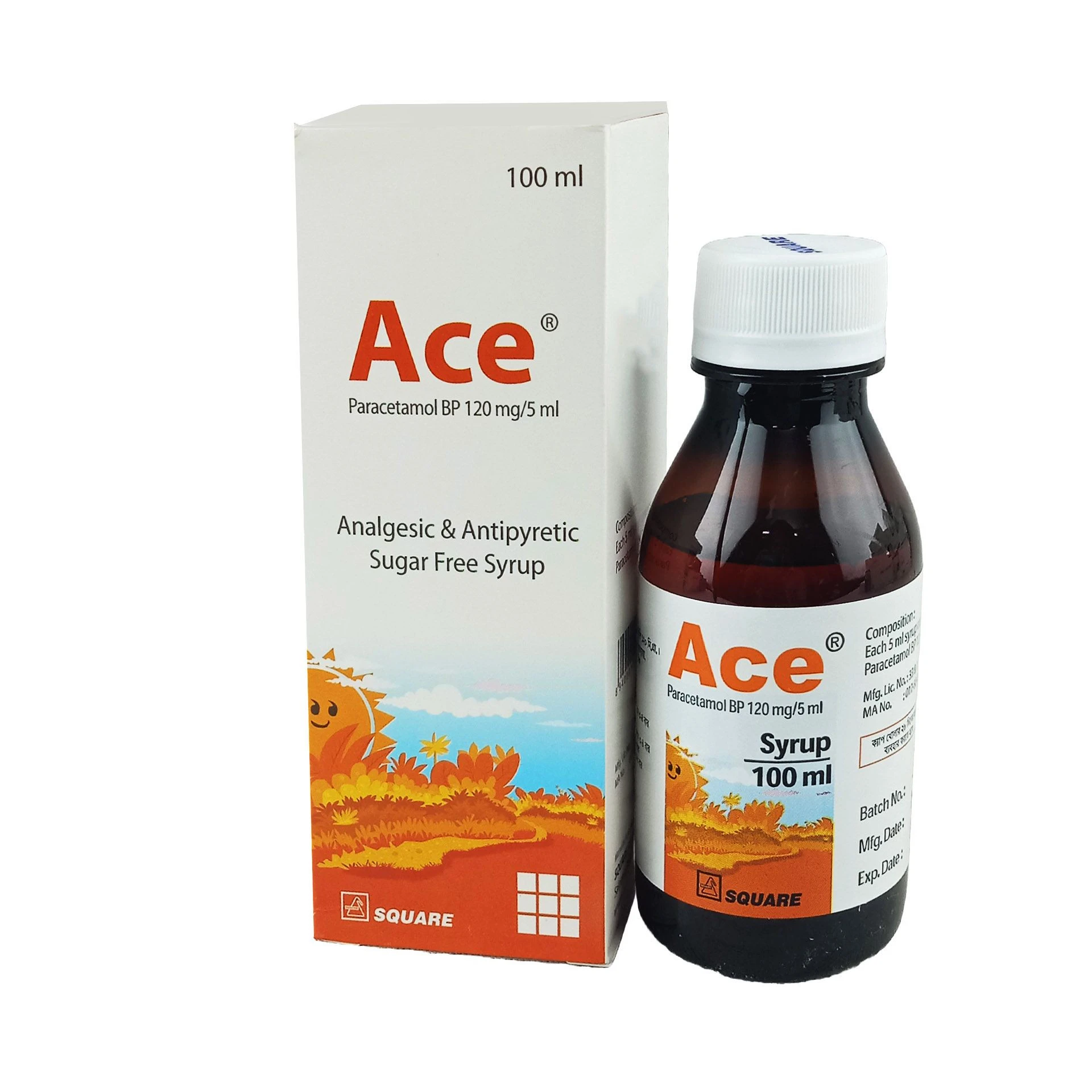
Indications
Solone is indicated in:
Rheumatic Disorders: Psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid
arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, acute and
subacute bursitis, acute nonspecific tenosynovitis, acute gouty arthritis,
post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
Endocrine Disorders: Primary or secondary adrenocortical
insufficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, nonsuppurative thyroiditis,
hypercalcemia associated with cancer.
Dermatologic Diseases: Pemphigus, bullous dermatitis
herpetiformis, severe erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, mycosis
fungoides, severe psoriasis.
Allergic States: Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis,
bronchial asthma, contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, serum sickness, drug
hypersensitivity reactions.
Respiratory Diseases: Symptomatic sarcoidosis, berylliosis,
fulminating, aspiration pneumonitis.
Hematologic Disorders: Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura,
secondary thrombocytopenia, acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia,
erythroblastopenia (RBC anemia).
Edematous States: To induce a diuresis or remission of
proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome, without uremia, of the idiopathic type
or that due to lupus erythematosus.
Gastrointestinal Diseases: Ulcerative colitis, regional
enteritis.
* রেজিস্টার্ড
চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Pharmacology
Prednisolone is a synthetic adrenocortical drug with
predominantly glucocorticoid properties. Prednisolone directly inhibits the
action of the Phospholipase A2 enzyme which is responsible for the production
of different inflammatory mediators like Leukotrienes, SRS-A, Prostaglandins
etc. Prednisolone is rapidly and well absorbed from the Gl tract following oral
administration. Prednisolone is 70- 90% protein-bound in the plasma and it is
eliminated from the plasma with a half-life of 2 to 4 hours. It is metabolized
mainly in the liver and excreted in the urine.
Dosage & Administration
Adult-
Nephrotic Syndrome:
Initial: 2 mg/kg/day (maximum 80 mg/day) in divided doses 3
to 4 times/day until urine is protein free for 3 consecutive days (maximum: 28
days); followed by 1 to 1.5 mg/kg/dose given every other day for 4 weeks.
Maintenance dose: 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/ dose given every other day
for 3 to 6 months.
Anti-inflammatory: 5 to 60 mg per day in divided doses 1 to
4 times/day.
Acute Asthma: 40-60 mg/day PO in single daily dose or
divided q12 hr for 3-10 days.
Allergic Conditions:
Day 1: 10 mg PO before breakfast, 5 mg after lunch and after
dinner, and 10 mg at bedtime.
Day 2: 5 mg PO before breakfast, after lunch, and after
dinner and 10 mg at bedtime.
Day 3: 5 mg PO before breakfast, after lunch, after dinner,
and at bedtime.
Day 4: 5 mg PO before breakfast, after lunch, and at
bedtime.
Day 5: 5 mg PO before breakfast and at bedtime.
Day 6: 5 mg PO before breakfast.
Pediatric-
Asthma:
1 year: Acute: 10 mg orally every 12 hours. Maintenance: 10
mg orally every other day.
1 to 4 years: Acute: 20 mg orally every 12 hours.
Maintenance: 20 mg orally every other day.
5 to 12 years: Acute: 30 mg orally every 12 hours.
Maintenance: 30 mg orally every other day.
12 years: Acute: 40 mg orally every 12 hours. Maintenance:
40 mg orally every other day.
Anti-inflammatory: 0.05 to 2 mg/kg/day divided 1 to 4
times/day.
Immunosuppression: 0.05 to 2 mg/kg/day divided 1 to 4
times/day.
* রেজিস্টার্ড
চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
The efficacy of Solone is reduced by Aminoglutethimide,
Antacids, Barbiturates, Carbamazepine, Griseofulvin, Mitotane, Phenylbutazone,
Phenytoin, Primidone and Rifampin. Solone reduces the amount of potassium in
the blood. Digitalis can cause Cardiac arrhythmias if hypokalemia occurs.
Immunization should be done very carefully.
Contraindications
Systemic infections unless specific anti-infective therapy
is employed. Hypersensitivity to any ingredient. Ocular herpes simplex because
of possible perforation.
Side Effects
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances: Sodium retention, fluid
retention, congestive heart failure in susceptible patients, potassium loss,
hypokalemic alkalosis, hypertension.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle weakness, steroid myopathy, loss of
muscle mass, osteoporosis, vertebral compression fractures, aseptic necrosis of
femoral and humeral heads, pathologic fracture of long bones.
Gastrointestinal: Peptic ulcer with possible perforation and
hemorrhage, pancreatitis, abdominal distention, ulcerative esophagitis.
Dermatologic: lmpaired wound healing, thin fragile skin,
petechiae and ecchymoses, facial erythema, increased
sweating, may suppress reactions to skin tests.
Neurological: Convulsions, increased intracranial pressure
with papilledema (cerebral pseudo-tumor) usually after treatment, vertigo,
headache.
Endocrine: Menstrual irregularities, development of
Cushingoid state, suppression of growth in children, secondary adrenocortical
and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress as in trauma
surgery or illness, decreased carbohydrate tolerance, manifestations of latent
diabetes mellitus, increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic
agents in diabetics.
Ophthalmic: Posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased
intraocular pressure, glaucoma, exophthalmos.
Metabolic: Negative nitrogen balance due to protein
catabolism.
Pregnancy & Lactation
This medicine is not recommended for use during pregnancy
unless considered essential by your doctor. It should only be used if the
expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the foetus.
Corticosteroids appear in breast milk and could suppress growth, interfere with
endogenous corticosteroid production or cause other unwanted effects.
Precautions & Warnings
Patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of
corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles.
Patients should also be advised that if they are exposed, medical advice should
be sought without delay.
ln patients on corticosteroid therapy subjected to unusual
stress, increased dosage of rapidly acting corticosteroids before, during and
after the stressful situation is indicated. Corticosteroids may mask some signs
of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. There may be
decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids
are used. Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subcapsular
cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance
the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can
cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased
excretion of potassium.
While on corticosteroid therapy, patient should not be
vaccinated against smallpox. Other immunization procedures should not be
undertaken in patients who are on corticosteroids, specially on high dose,
because of possible hazards of neurological complications and a lack antibody
response.
Children who are on drugs, which suppress the immune system,
are more susceptible to infections than healthy children.
Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have more serious
or even fatal course in non-immune children or adults on corticosteroids.
Use in Special Populations
Pediatric use: ln the treatment of endocrine disorders such
as primary and secondary adrenocortical insufficiency in infancy, mineralocorticoid
supplementation is of particular importance. lnfants born to mothers who have
received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be
carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism. lmmunization procedures should
not be undertaken in patients who are on corticosteroids. Pediatric patients
who are on drugs which suppress the immune system are more susceptible to
infections than healthy pediatric patients. Chickenpox and measles, for
example, can have more serious or even fatal course in non-immune patients on
corticosteroids. Growth and development in pediatric population on prolonged
corticosteroid therapy should be carefully observed. See contraindications and
warnings for complete information.
Overdose Effects
Adverse effects related to prednisone normally develop only
after prolonged use of doses in excess of the normal physiological requirement.
Treatment is symptomatic and where possible the prednisone dose should be
reduced gradually.
Therapeutic Class
Glucocorticoids
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool and dry place, protected from light. Keep
out of the reach of the children.
No review given yet!
 Fast Delivery all across the country
Fast Delivery all across the country
 Safe Payment
Safe Payment
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 100% Authentic Products
100% Authentic Products





You need to Sign in to view this feature
This address will be removed from this list