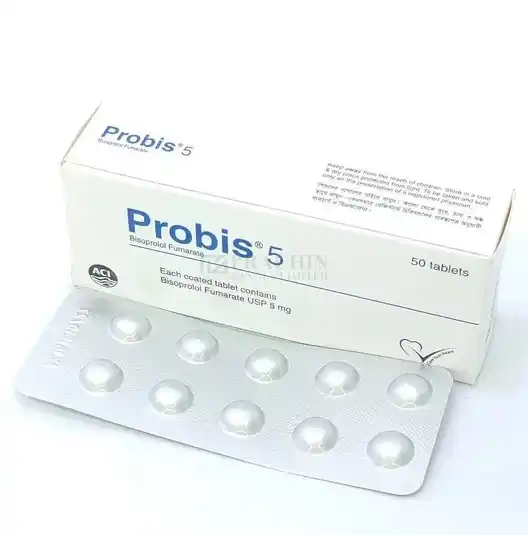
Indications
Probis tablet is indicated in-
Hypertension
Angina
Moderate to severe heart failure
Probis is not recommended for the emergency treatment of
hypertensive crises.
* রেজিস্টার্ড
চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Pharmacology
Bisoprolol Fumarate is the most selective ß1 blocker. It displays
highest level of affinity for the ß1 receptor than any other beta-blocker
available up to now. Selectively blocks ß1 adrenergic receptor in the heart and
vascular smooth muscle and reduces heart rate and cardiac output resulting in
decrease of arterial hypertension. Lipid metabolism can be adversely affected
by ß-blockers, in patients with non-ß1 selective ß1-blocker, but Bisoprolol
does not cause any change in the cholesterol fraction including the
cardioprotective HDL-cholesterol, in long-term therapy.
The pharmacokinetic properties of Bisoprolol provide the
prerequisite for a single daily dose and ensure an extremely low inter and
intra-individual variability of the plasma concentration profiles. The high
therapeutic reliability of Bisoprolol is based on these properties.
Absorption and bioavailability: Bisoprolol is almost
completely (>90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The high
absorption rate and the small first-pass effect (<10%) lead to an absolute
bioavailability of 88%. Concomitant food intake does not affect the absorption.
Distribution: Bisoprolol is extensively distributed. The medium distribution
volume is 3.51/kg.
Metabolism: Bisoprolol is metabolized via oxidative pathways
with no subsequent conjugation. All metabolites, being very polar, are renally
eliminated. The major metabolites in human plasma and urine were found to be
without pharmacological activity. In vitro data from studies in human liver
microsomes show that Bisoprolol is primarily metabolized via CYPSA4 (-95%) with
CYP2D6 having only a minor role.
Elimination: The clearance of Bisoprolol is balanced between
renal elimination of the unchanged molecule (-50%) and hepatic metabolism
(-50%) to metabolites which are also renally excreted. The total clearance of Bisoprolol
is approximately 15 I/h. Bisoprolol has an elimination half-life of 10-12
hours.
Dosage & Administration
Adult: In the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension,
Bisoprolol fumarate must be individualized to the needs of the patient. The
usual starting dose is 5 mg once daily either added to a diuretic or alone. If
the response to 5 mg is inadequate, the dose may be increased to 10 mg and
then, if necessary, to 20 mg once daily. An appropriate interval for dose
titration is 2 weeks. Increasing the dose beyond 20 mg once daily produces only
a small incremental benefit.
Children: Safety and effectiveness in children have not been
established.
Patients With Renal or Hepatic Impairment: In patients with
hepatic impairment (hepatitis or cirrhosis) or renal dysfunction (creatinine
clearance less than 40 mL/min) as in other patients, the initial daily dose
should be 5 mg. Because of the possibility of accumulation, caution must be
used in dose titration. Since limited data suggest that bisoprolol fumarate is
not dialysable, drug replacement is not necessary in patients undergoing
dialysis.
Geriatrics: In the elderly, it is not usually necessary to
adjust the dose, unless there is also significant renal or hepatic dysfunction
* রেজিস্টার্ড
চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
Other β-blocking Agents: Probis should not be combined with
other β-blocking agents.
Catecholamine-Depleting Drugs: Patients receiving
catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine or guanethidine, should be
monitored closely because the added β-adrenergic blocking action of Probis may
produce excessive reduction of sympathetic activity.
Centrally Active Antihypertensive Agents: β-blockers may
exacerbate the rebound hypertension which can follow the withdrawal of
clonidine. If the two drugs are coadministered, the β-blocker should be
withdrawn several days before discontinuing clonidine. If replacing clonidine
by β-blocker therapy, the introduction of β-blockers should be delayed for
several days after clonidine administration has stopped (see also prescribing
information for clonidine).
Antiarrhythmic Agents: Probis should be used with care when
myocardial depressants or inhibitors of A-V conduction, such as certain calcium
antagonists (particularly of the phenyl alkylamine (verapamil) and
benzothiazepine (diltiazem) classes), or antiarrhythmic agents, such as
disopyramide, are used concurrently.
Calcium Channel Blockers: Combined use of β-blockers and
calcium channel blockers with negative inotropic effects can lead to
prolongation of S-A and A-V conduction, particularly in patients with impaired
ventricular function or conduction abnormalities. This may result in severe hypotension,
bradycardia and cardiac failure.
Contraindications
In patients with cardiogenic shock, overt heart failure,
second or third degree A-V block, right ventricular failure secondary to
pulmonary hypertension and sinus bradycardia.
Side Effects
Medicines and their possible side effects can affect
individual people in different ways. The following are some of the side effects
that are known to be associated with this medicine. Just because a side effect
is stated here does not mean that all people using this medicine will
experience that or any side effect. Fatigue, dizziness, headache, disturbances
of the gut such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation or abdominal pain.
Cold or numb extremities, e.g; hands and feet. Muscle weakness or cramps. Slower
than normal heart breathing difficulties due to a narrowing of the airways
(bronchospasm) in people with asthma or COPD.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: Bisoprolol fumarate was not teratogenic in rats
at doses up to 150 mg/kg/day, which is 375 times the maximum recommended human
daily dose. Bisoprolol fumarate was fetotoxic (increased late resorptions) at
50 mg/kg/day and maternotoxic (decreased food intake and body-weight gain) at
150 mg/kg/day. Bisoprolol fumarate was not teratogenic in rabbits at doses up
to 12.5 mg/kg/day, which is 31 times the maximum recommended human daily dose,
but was embryolethal (increased early resorptions) at 12.5 mg/kg/day. There are
no studies in pregnant women. Bisoprolol fumarate should be used during
pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the
fetus.
Lactation: Small amounts of bisoprolol fumarate (<2% of
the dose) have been detected in the milk of lactating rats. It is not known
whether this drug is excreted in human milk. If use of bisoprolol fumarate is
considered essential, then mothers should stop nursing.
Precautions & Warnings
Impaired renal or hepatic function use caution in adjusting
the dose of Probis in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. While taking
beta-blockers, patients with a history of severe anaphylactic reaction to a
variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated challenge, accidental,
diagnostic, or therapeutic. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual
doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reactions.
Therapeutic Class
Anti adrenergic agent (Beta blockers), Beta-adrenoceptor
blocking drugs, Beta-blockers
Storage Conditions
Keep in a dry place away from light and heat. Keep out of
the reach of children.